线性表的实现
本文共 27089 字,大约阅读时间需要 90 分钟。
- 见文章:
二、数组实现线性表的方法
方式一
- 从数组的头端实现
- 例如有一个数组element[10],我们可以将元素{5,2,4,8,1}从其索引0处作为线性表的头开始实现,线性表的方向从左至右
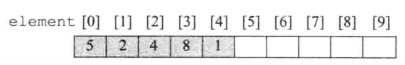
方式二
- 从数组的尾端实现
- 接方式一,我们将数组element的最后一个索引处作为线性表的头开始实现,线性表的方向从右至左
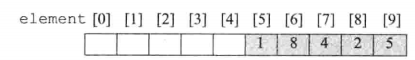
方式三
- 从数组的指定索引处实现,我们可以从数组的指定索引处作为线性 表的头部开始实现
- 公式为:localtion(i)=(localtion(0)+i)%arrayLength
- localtion(0)是选取的线性表在数组中的第一个位置
- arrayLength是数组的长度
- 例如,下面我们将数组element的索引7作为线性表的头部开始从左至右实现,当元素超出数组的长度时,将元素从数组的索引0处开始插入。此处我们的公式为,localtion(i)=(7+i)%10
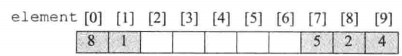
三、编码实现
异常类实现(illegalParameterValue)
- 这个异常类主要用来处理函数的参数异常
class illegalParameterValue { private: string message; public: illegalParameterValue() : message( "Illegal Parameter Value") {} illegalParameterValue( const char* s) :message(s) {} const char *what() { return message.c_str(); } }; 修改数组长度函数(changeLength)
- 功能:该函数用来改变原来数组的长度,在函数中我们创建一个新的数组,然后将原数组拷贝进新数组,然后释放原数组所指向的地址空间(这个函数是全局函数,并不属于某一类)
- 参数:
- 参数1:数组指针引用
- 参数2:原数组的长度
- 参数3:新数组长度
- 函数的时间复杂度:创建一个长度为newLength的数组所需时间为Θ(1)。copy的时间复杂度为Θ(length)。所以,下面函数的总的时间复杂度为Θ(length)
template< typename T> void changeLength(T* &a, int oldLength, int newLength) { if (newLength < 0) { throw illegalParameterValue( "new length must be >=0"); } T *arr = new T[newLength]; int length = min(oldLength, newLength); copy(a, a + length, arr); delete [] a; a = arr; } 线性表类实现
- linearList是线性表的纯虚函数,其含有一系列线性表的操作方法;arrayList继承于linearList,是线性表的数组实现形式的类,其重写linearList的虚函数,并添加了自己的一些数据成员和方法
template< typename T> class linearList { public: virtual ~linearList() {}; //当线性表为空时返回true virtual bool empty() const = 0; //返回线性表的元素个数 virtual int size() const = 0; //返回索引theIndex的元素 virtual T& get(int theIndex)const = 0; //返回元素theElement第一次出现时的索引 virtual int indexOf(const T& theElement) const = 0; //删除索引为theIndex的元素 virtual void earse(int theIndex) = 0; //把theElement插入线性表中索引为theIndex的位置上 virtual void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) = 0; //把线性表插入输出流out virtual void output(ostream& out)const = 0; }; template< typename T> class arrayList : public linearList { public: arrayList( int initialCapacity = 10); //构造函数 arrayList( const arrayList & other); //拷贝构造 ~arrayList(); //析构函数 bool empty()const override; int size()const override; T& get(int theIndex)const override; int indexOf(const T& theElement)const override; void earse(int theIndex)override; void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)override; void output(ostream& out)const override; //返回数组的容量 int capacity()const; protected: T *element; //存储线性表的一维数组 int arrayLength; //一位数组的容量 int listSize; //当前线性表的元素个数 protected: void checkIndex(int theIndex)const; //检查索引theIndex是否有效 }; 构造函数
- 构造函数首先判断传入的数组长度是否有效,如果无效抛出一个异常。如果有效,初始化数组
- 时间复杂度:
- 如果T是基本数据类型,那么构造函数的时间复杂度是O(1)
- 如果T是用户自定义类型,那么构造函数的时间复杂度是O(initialCapacity)。因为数组的每一个元素都是自定义类型,需要调用构造函数
template< typename T> arrayList::arrayList( int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity < 1) { ostringstream s; s << "Initial capacity is " << initialCapacity << ",Must be >0"; throw illegalParameterValue(s.str().c_str()); //str()将ostringstream转换为string,c_str()将string转换为const char* } arrayLength = initialCapacity; element = new T[arrayLength]; listSize = 0; }
拷贝构造函数
- 初始化一些数据成员,然后调用copy函数进行拷贝
- 时间复杂度:为O(listSize),其中listSize是要复制的线性表的大小
template< typename T> arrayList::arrayList( const arrayList & other) { arrayLength = other.arrayLength; listSize = other.listSize; element = new T[arrayLength]; copy(other.element, other.element + listSize, element); }
析构函数
template< typename T> arrayList::~arrayList() { delete[] element; }
empty、size、capacity
- 下面3个函数的时间复杂度都是O(1)
template< typename T> bool arrayList::empty() const { return listSize == 0; } template< typename T> int arrayList ::size() const { return listSize; } template< typename T> int arrayList ::capacity() const { return arrayLength; }
检索下标合格性(checkIndex)
- 时间复杂度是Θ(1)
template< typename T> void arrayList::checkIndex( int theIndex) const { if ((theIndex< 0) || (theIndex>=arrayLength)) { ostringstream s; s << "index=" << theIndex << ",size=" << arrayLength; throw illegalParameterValue(s.str().c_str()); } }
返回指定索引处值(get)
- 时间复杂度是Θ(1)
template< typename T> T& arrayList::get( int theIndex) const { checkIndex(theIndex); return element[theIndex]; }
返回元素在线性表的指定位置(indexOf)
- 时间复杂度是O(listsize)
template< typename T> int arrayList::indexOf( const T& theElement) const { int index; //find成功返回查找的迭代器位置,失败返回参数2 index = ( int)(find(element, element + listSize, theElement) - element); //如果没有找到 if (index == listSize) { return - 1; } else return index; }
删除指定索引处的元素(earse)
- 时间复杂度:
- 如果checkIndex抛出异常,那么时间复杂度是Θ(1)
- 如果元素存在,那么要移动的元素个数是listSize-theIndex,所以时间复杂度是Θ(listSize-theIndex)(假设每一个元素移动的时间复杂度是O(1))
- 因此,全部时间复杂度是O(listSize-theIndex)
template< typename T> void arrayList::earse( int theIndex) { checkIndex(theIndex); //参数12分别为要移动的区间的起始迭代位置和尾后迭代器 copy(element+ theIndex+ 1, element+ listSize, element + theIndex); element[--listSize].~T(); }
在指定索引处插入元素(insert)
- 这里没有没有使用copy函数来移动元素,而是使用copy_backward来移动元素
- 时间复杂度:
- 如果抛出异常,那么时间复杂度是Θ(1)
- 如果数组需要加长,那么时间复杂度是Θ(arrayLength)=Θ(listSize)
- copy_backward移动数组元素,时间复杂度是Θ(listSize-theIndex)
- 综上所述,下面函数的时间复杂度是O(listSize)
template< typename T> void arrayList::insert( int theIndex, const T& theElement) { if ((theIndex< 0) || (theIndex>listSize)) { ostringstream s; s << "index=" << theIndex << ",size=" << arrayLength; throw illegalParameterValue(s.str().c_str()); } if (listSize == arrayLength) { changeLength(element, arrayLength, arrayLength * 2); arrayLength *= 2; } //会复制前两个迭代器参数指定的序列。第三个参数是目的序列的结束迭代器 copy_backward(element+ theIndex, element+ listSize, element + listSize+ 1); element[theIndex] = theElement; listSize++; }

打印线性表元素(output)
- 时间复杂度:如果插入一个元素的时间是O(1),那么这个代码的时间复杂度是O(listSize)
template< typename T> void arrayList::output(ostream& out) const { copy(element, element+ listSize,ostream_iterator (out, " ")); }
重载流插入符<<
- 这个是全局函数
template< typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList& x) { x.output(out); return out; }
改写earse函数
- 为了能够在数组元素减少时释放一些数组空间,我们修改earse方法,当listSize<arrayLength/4时,将数组的长度减少到arrayLength/2
template< typename T> void arrayList::earse( int theIndex) { checkIndex(theIndex); copy(element+ theIndex+ 1, element+ listSize, element + theIndex); if (listSize < (arrayLength / 4)) { changeLength(element, arrayLength, arrayLength / 2); } element[--listSize].~T(); }
演示效果
int main() { linearList< int>* list = (linearList< int>*) new arrayList< int>(); cout << "Current size:"<< list->size()<< "\n"<< endl; cout << "Current list is:"; list->output( cout); list->insert( 0, 1); list->insert( 0, 2); cout << "Current size:" << list->size() << "\n" << endl; cout << "Current list is:"; list->output( cout); cout << "The index of 2 is:" << list->indexOf( 2)<< "\n"<< endl; list->earse( 1); cout << "Current list is:"; list->output( cout); return 0; } 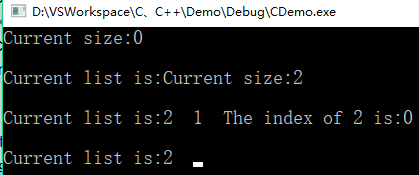
- 备注:此处我们使用抽象类linearList指向与派生类arrayList,所以不能使用基类的capacity()函数
四、迭代器的设计
- 我们定义了一个双向迭代器。这个迭代器是类arrayList的公有成员,此外我们还为arrayList定义了两个公有方法begin()和end()
template< typename T> class arrayList : public linearList{ /*...*/ public: class iterator; iterator begin() { return iterator(element); } iterator end() { return iterator(element + listSize); } class iterator { public: typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; typedef T value_type; typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; typedef T* pointer; typedef T& reference; public: iterator(T* thePosition = 0) { position = thePosition; } /*~iterator() { //析构函数出错,不知道为什么,待续 if (position) { delete[] position; position = nullptr; } }*/ T& operator*() const { return *position; } T* operator->() const { return &*position; } iterator& operator++() { ++position; return * this; } iterator operator++( int) { iterator old = * this; ++position; return old; } iterator& operator--() { --position; return * this; } iterator operator--( int) { iterator old = * this; --position; return old; } bool operator==( const iterator other) const { return position == other.position; } bool operator!=( const iterator other) const { return position != other.position; } protected: T *position; }; /*...*/ };
演示案例
int main() { arrayList< int> list; list.insert( 0, 1); list.insert( 1, 2); list.insert( 2, 3); list.insert( 3, 4); arrayList< int>::iterator iter; for (iter = list.begin(); iter != list.end(); ++iter) { cout <<*iter << " "; } cout << "\n" << endl; return 0; } 
五、总结
- 这次在设计的时候,迭代器的析构函数总是出错,不知道原因是什么,于是我把其注释掉了(待续解决)
- 迭代器的知识见:
- copy、insert算法见文章:
- 代码下载:
你可能感兴趣的文章
Flutter UI基础 - 侧拉抽屉菜单
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - AppBar中标题文字如何居中
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - Drawer 抽屉视图与自定义header
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 点击展开和关闭
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - GridView
查看>>
Flutter UI - 打造一个圆形滑块(Slider)
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 分割线效果实现
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - DecoratedBox组件
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 使用InkWell给任意Widget添加点击事件
查看>>
OC WKWebView的使用
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - Image.asset 图片铺满布局
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - Row、Column详解
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 添加背景图片
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 布局之Row/Column/Stack
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 层叠布局Stack的使用
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - webview 使用和交互
查看>>
Flutter UI基础 - 时间选择器
查看>>
Idea - 创建Java类时,自动在文件头中添加作者和创建时间
查看>>
Docker - ASP.NET Core Docker部署
查看>>
Docker - 容器运行 .Net Core
查看>>